Shop By Category
Trailokya Vijaya Vati
Sale price₹ 229 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 239
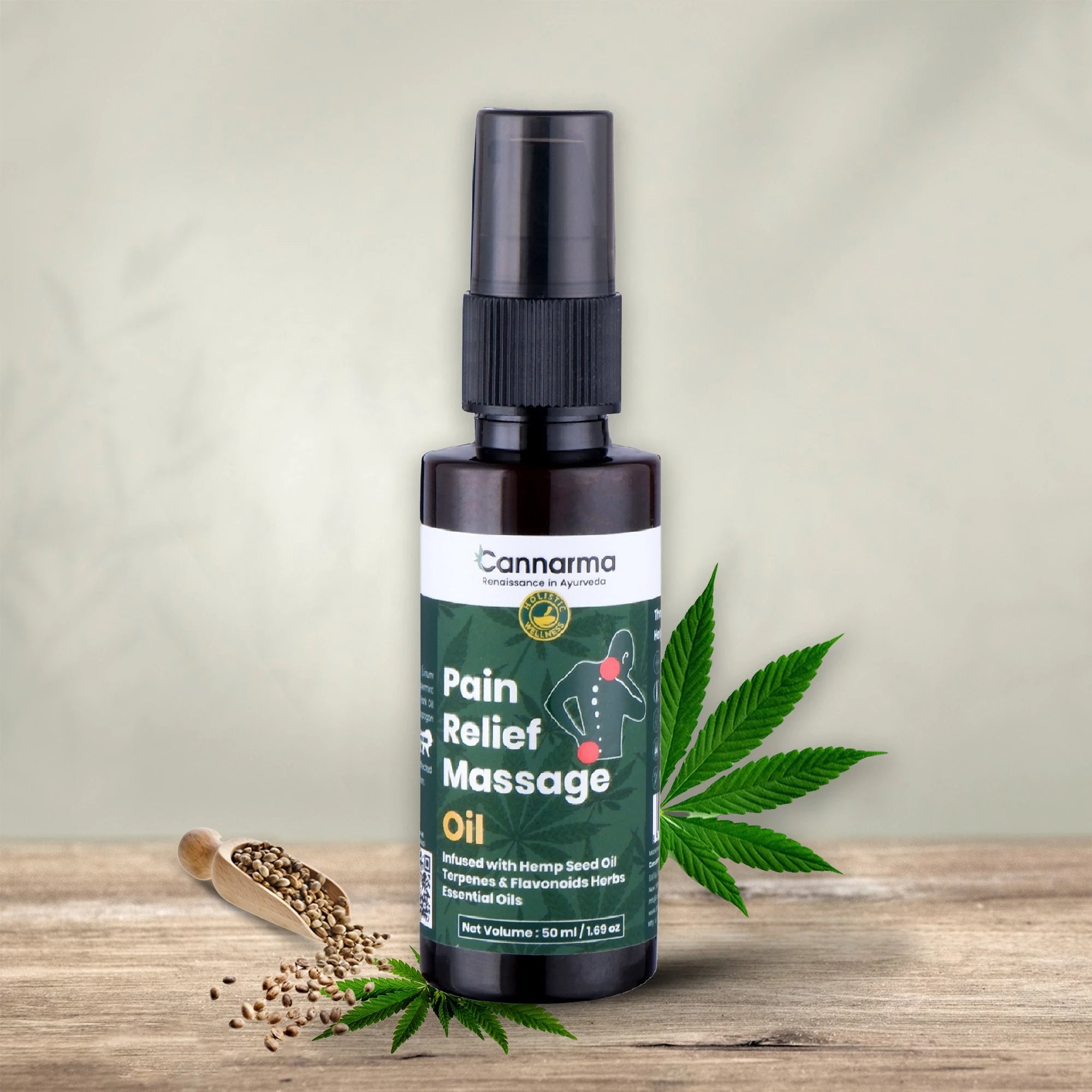
Hemp Pain Relief Massage Oil (50ml)
Sale price₹ 379 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 599
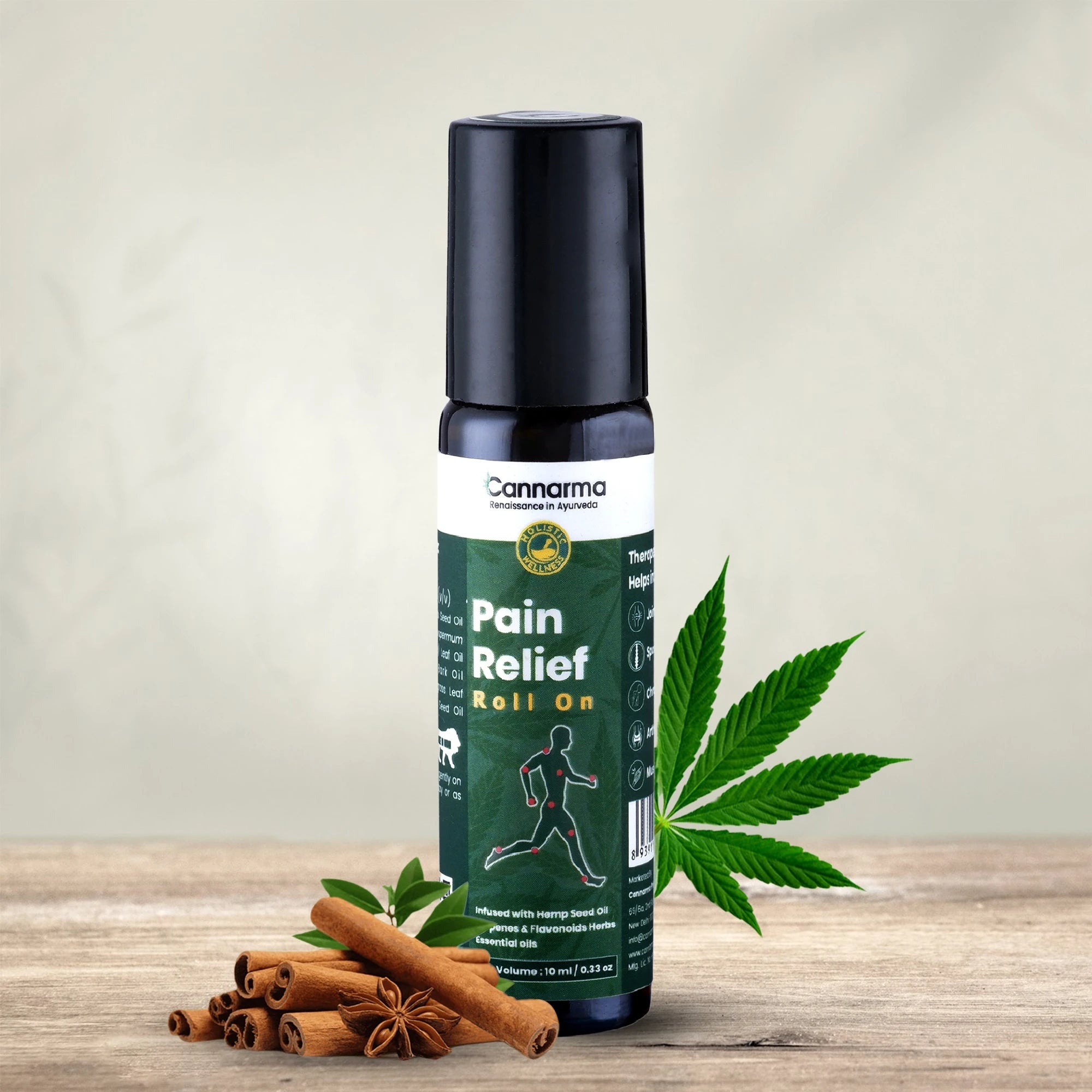
Hemp Pain Relief Roll On (10ml)
Sale price₹ 206 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 249
Hemp Pain Relief Balm (15g)
Sale price₹ 220 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 249
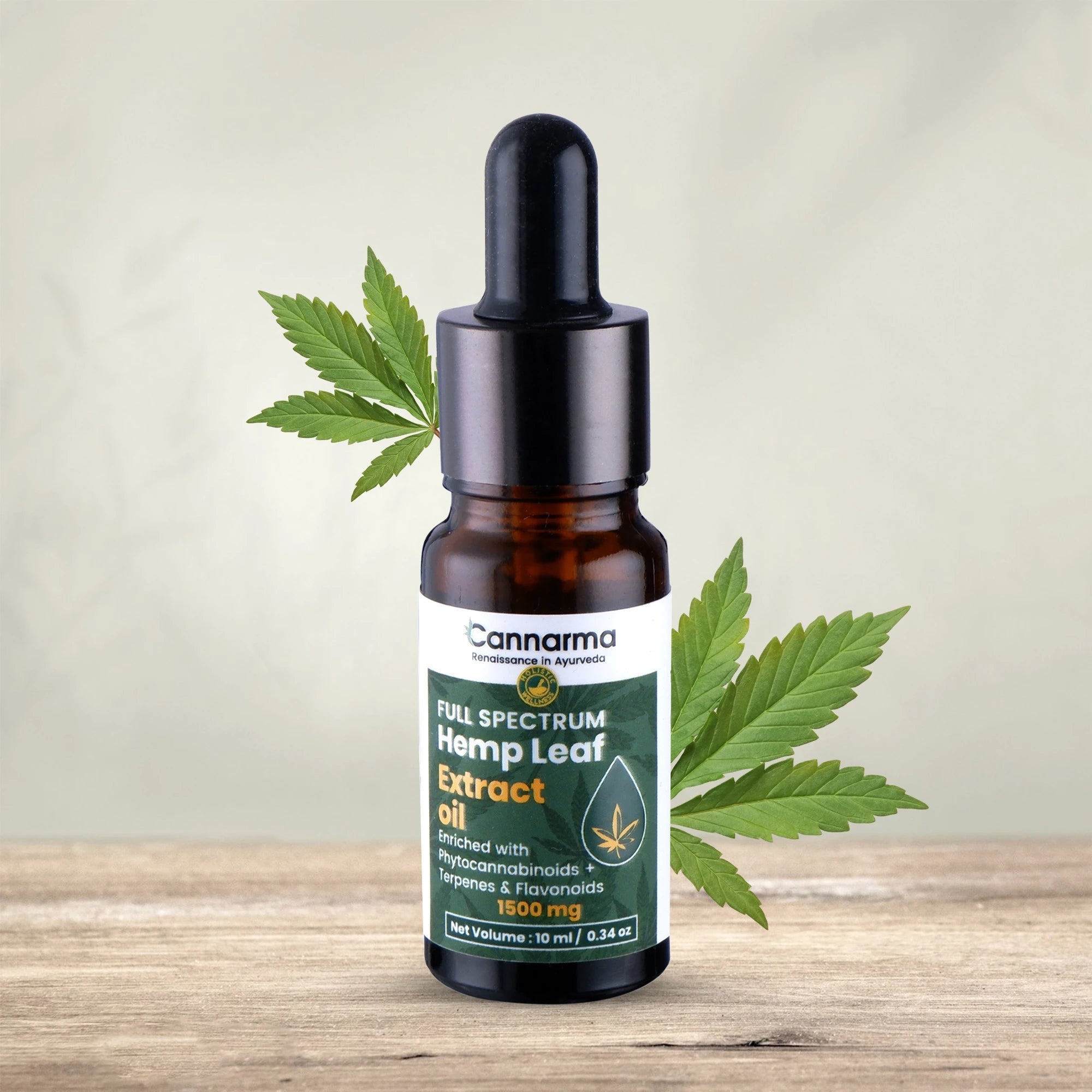
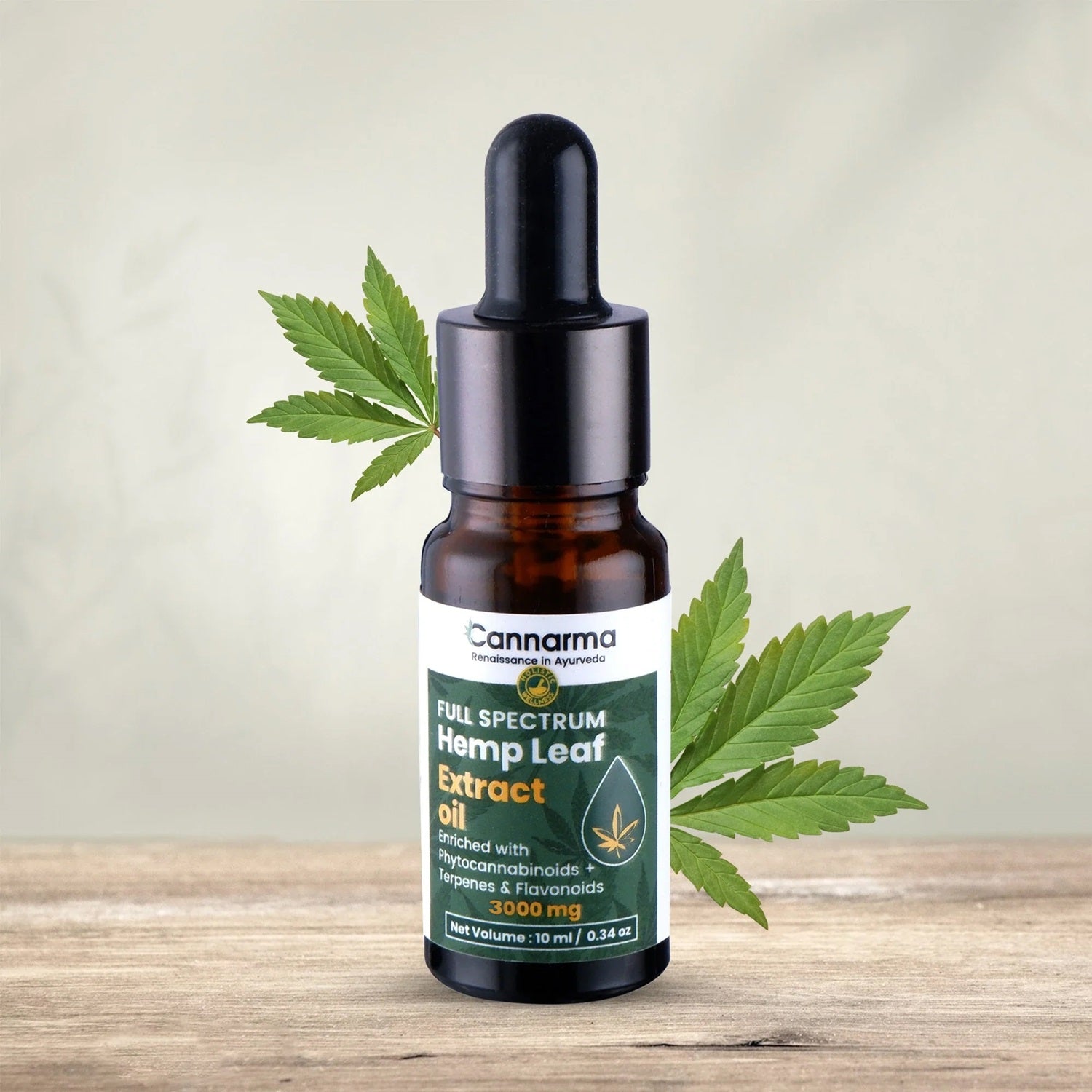
Hemp Extract CBD Oil (1500mg)
Sale priceFrom ₹ 2,049 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 2,100
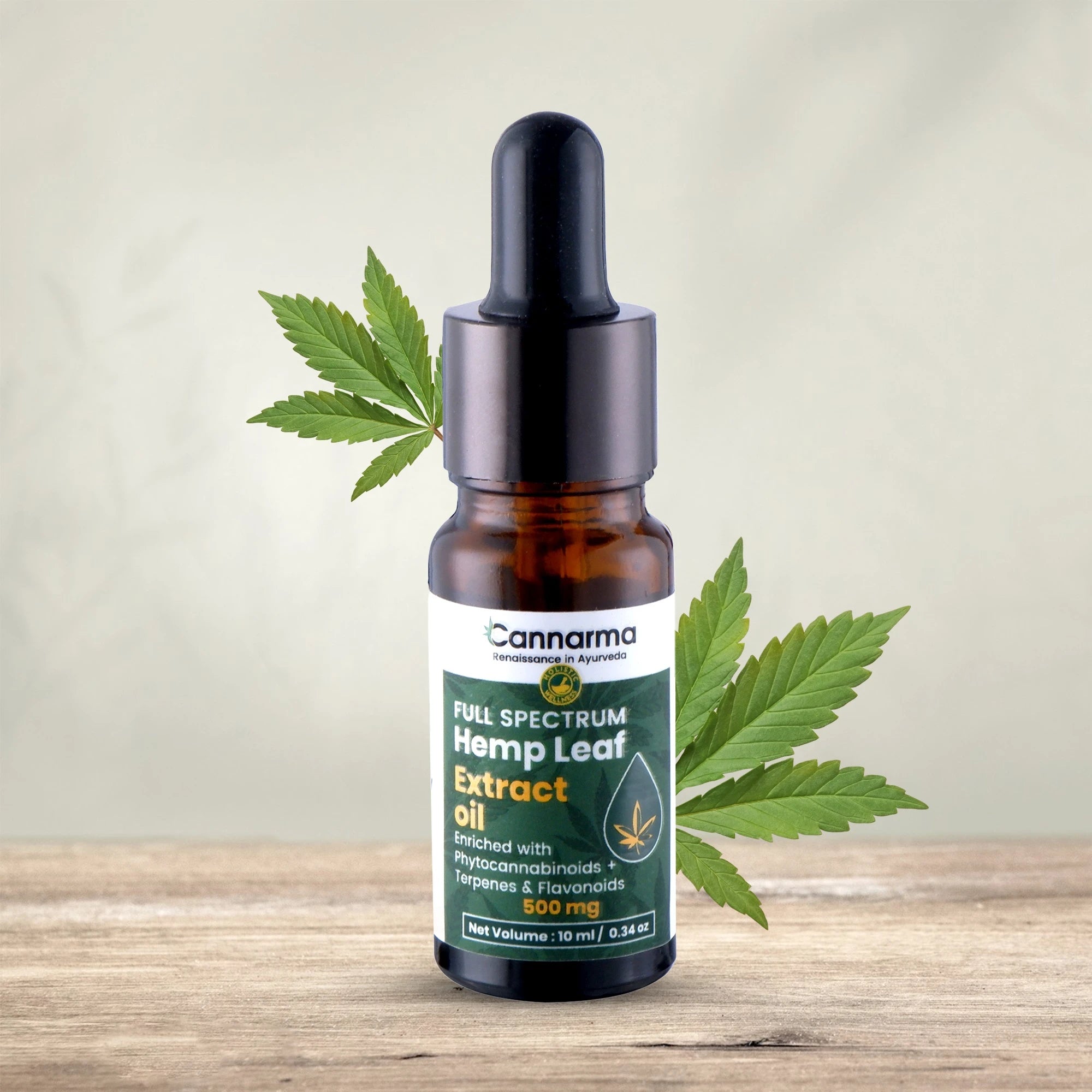
Hemp Extract CBD Oil (500mg)
Sale priceFrom ₹ 1,479 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 1,500
Hemp Extract CBD Oil (3000mg)
Sale priceFrom ₹ 3,299 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 3,999
Pure Himalayan Shilajit (10g)
Sale priceFrom ₹ 599 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 1,499
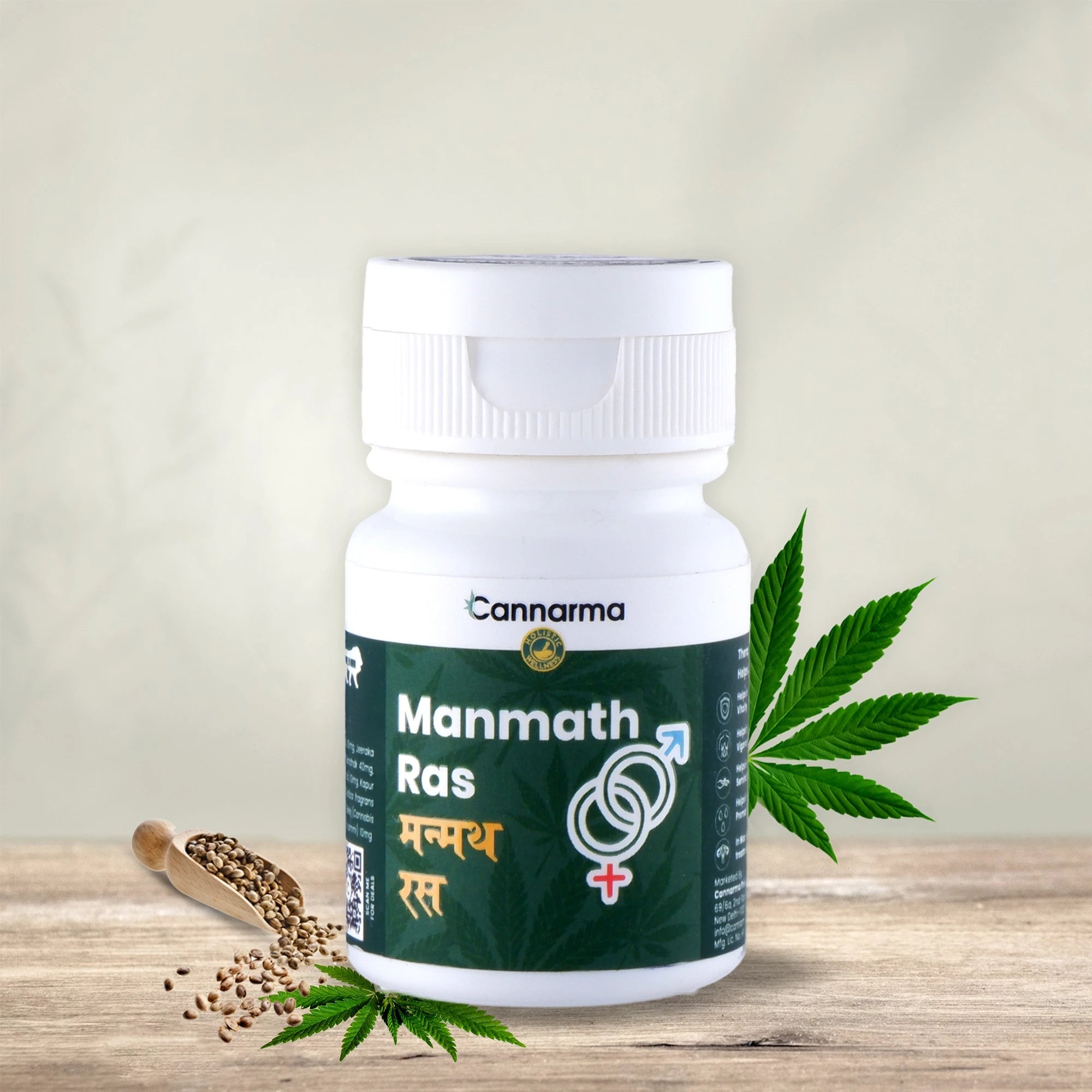
Manmath Ras Tablet
Sale priceFrom ₹ 169 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 199
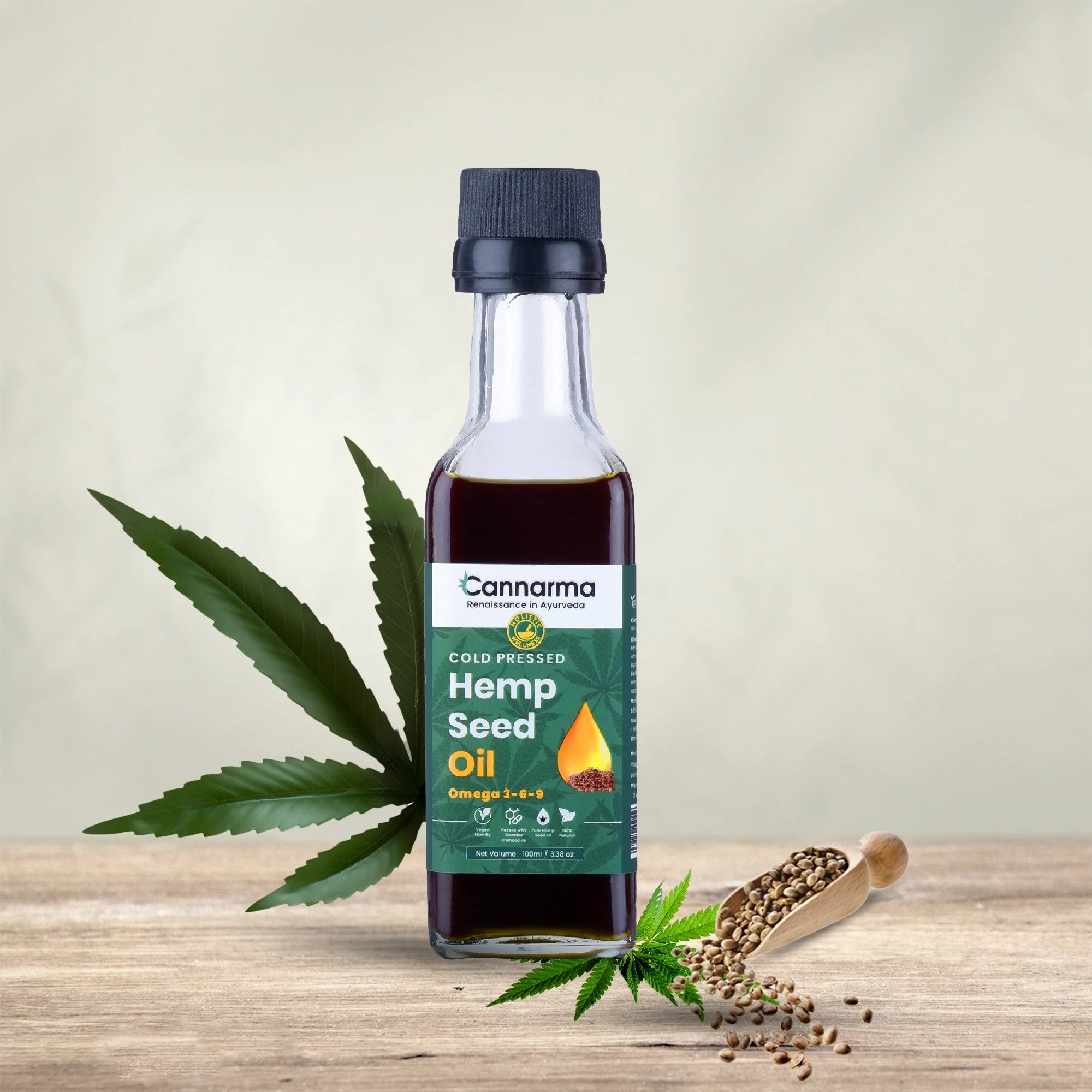
Hemp Seed Oil | Omega 3,6,9 (100ml)
Sale price₹ 404 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 499
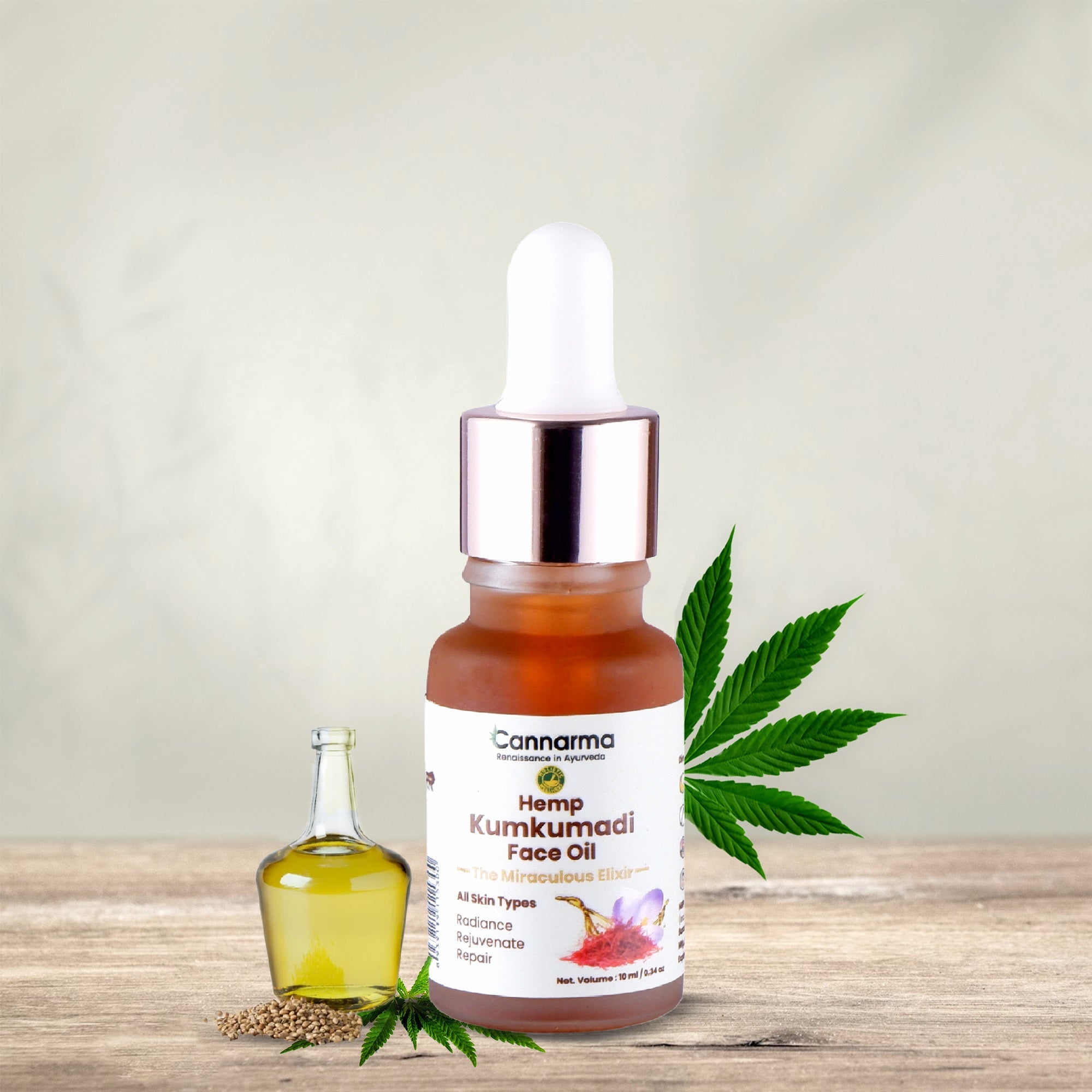
Hemp Kumkumadi Face Oil
Sale price₹ 599 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 999
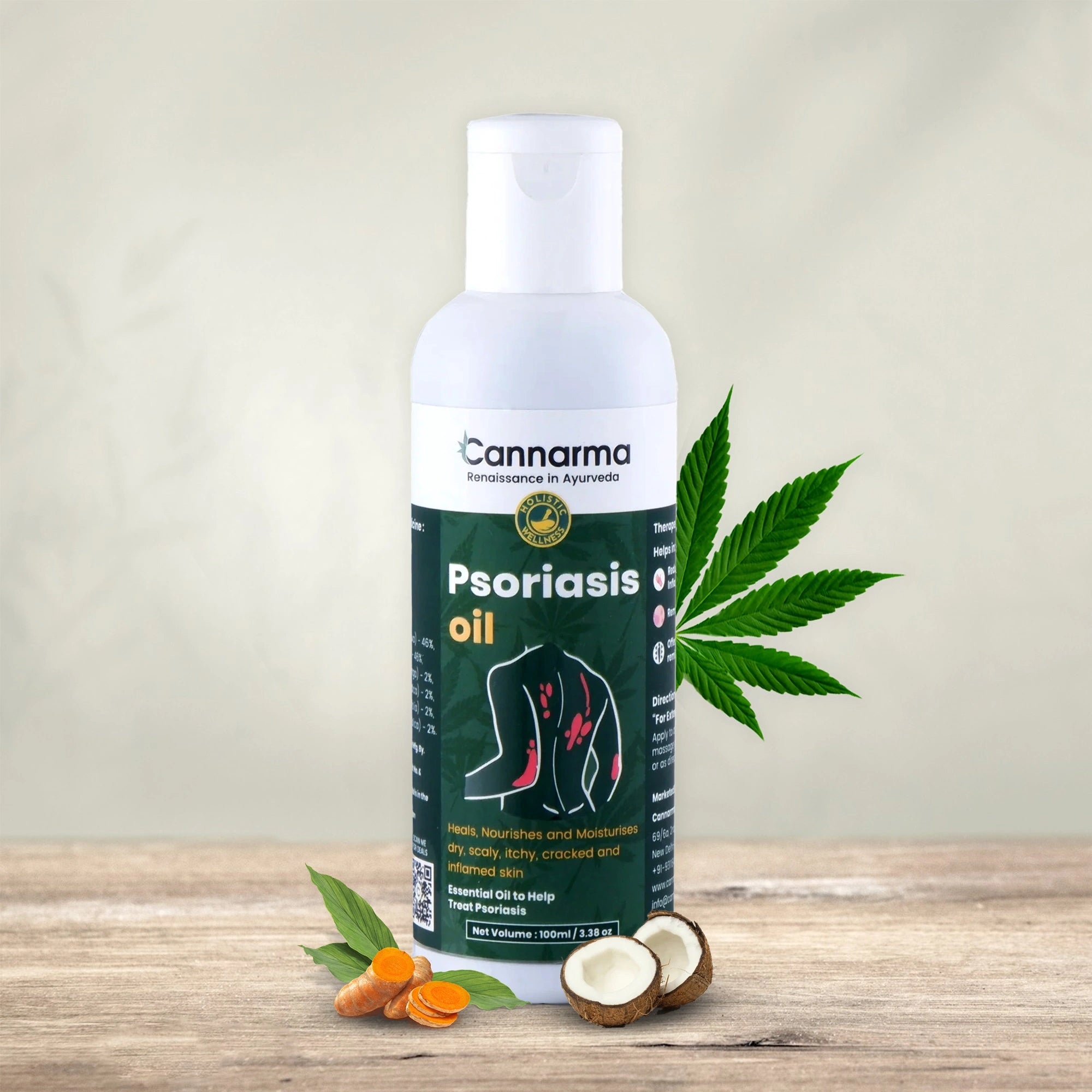
Hemp Psoriasis Oil (100ml)
Sale price₹ 569 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 677
Hemp Hair Oil (50ml)
Sale price₹ 305 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 399
Popular Cannabis Oil Products

Life is Better with Hemp
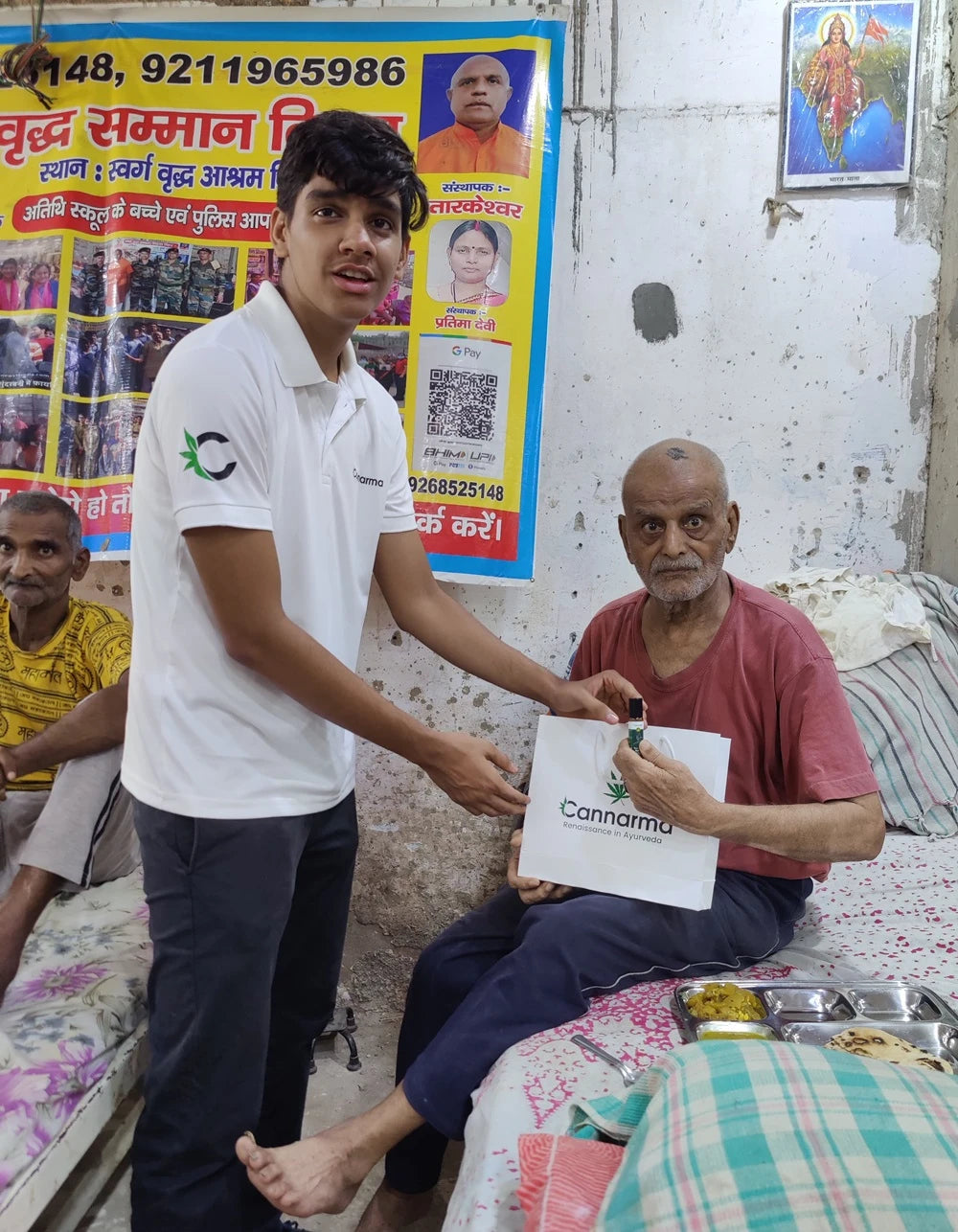



2% for People & Nature
With every purchase, you’re not just buying a product, you’re planting a seed for a better tomorrow.
Join us in our journey where 2% returns to the people and nature, nurturing growth and greenery for generations to come.
100% Natural
Non-Addictive
Long-Lasting Results
Best Sellers
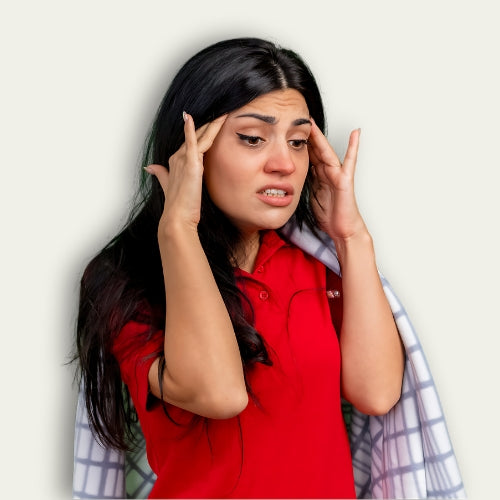

Hemp Pain Relief Balm (15g)
Sale price₹ 220 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 249

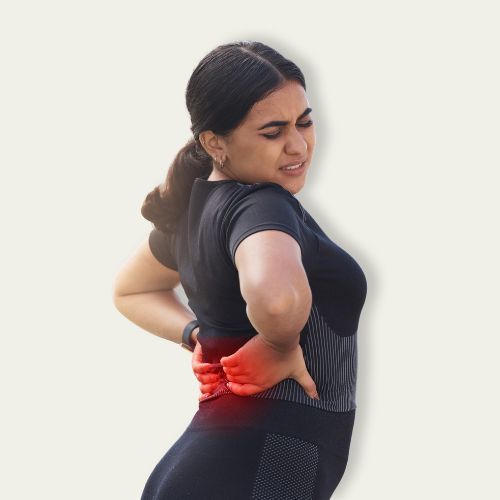
Hemp Pain Relief Massage Oil (50ml)
Sale price₹ 379 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 599

Hemp Pain Relief Roll On (10ml)
Sale price₹ 206 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 249

Hemp Pain Relief Balm (15g)
Sale price₹ 220 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 249

Hemp Pain Relief Massage Oil (50ml)
Sale price₹ 379 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 599

Hemp Pain Relief Roll On (10ml)
Sale price₹ 206 M.R.P.
Regular price₹ 249






Proudly Made in India

Loved by 15,000+ Customers
Across The World!
Real experiences that turned our shoppers into our Family.